Incorrect DNS and GEO IP address of proxy-server
 If you don't know about what one flaw in the MaxMind database led 82-year-old Joyce Taylor of Kansas to, it is highly recommended that you read more about it on news sites.
If you don't know about what one flaw in the MaxMind database led 82-year-old Joyce Taylor of Kansas to, it is highly recommended that you read more about it on news sites.
Let's analyze the situation briefly and without unnecessary details: because of incorrect entries in the IP-address coordinate databases, a resident of a small farm in Kansas was subjected for several years to telephone threats, stalking, and visits from agents of the FBI and tax services. How an IP address database is involved is a logical question, so we'll try to explain. This fuss happened because the company that owns and administers the MaxMind database decided to simplify one of the pointers to geographic coordinates to a shortened form, and so about 600 million IP addresses were directed to this unfortunate farm, which caused the owner to get into trouble.
The "small flaw", which resulted in a nervous breakdown for Joyce Taylor, has already been corrected, but the information remained on the Internet about it, and after it the consequences, and this is not only about the coordinates of individual servers, there is a more global problem, which is what we are talking about today.
Where does an IP address get its country affiliation information from?
Providers offer mobile, residential and server proxies for rent. The latter are the most popular, as they are excellent for surfing, parsing and multi-accounting. Usually providers offer dozens of countries for rent. For example, US proxies are ideal for getting access to all popular social networks and applications. Sometimes users use specific countries for specific purposes: for example, to access a site that is available only to residents of a particular country, or to connect to a local server and play with the lowest ping.
In general, some users just need to change IP for anonymity, and some need specific geolocation. The latter sometimes check proxy data after renting it from services such as 2ip.io.
If you look specifically at the IP-address, it does not carry any information about belonging to one or another ISP, city and country, as well as information about coordinates, and services that determine GEO by IP, for example, MaxMind (https://www.maxmind.com/en/geoip-demo), just have a database of addresses and their locations, coordinates, belonging to an ISP, etc.
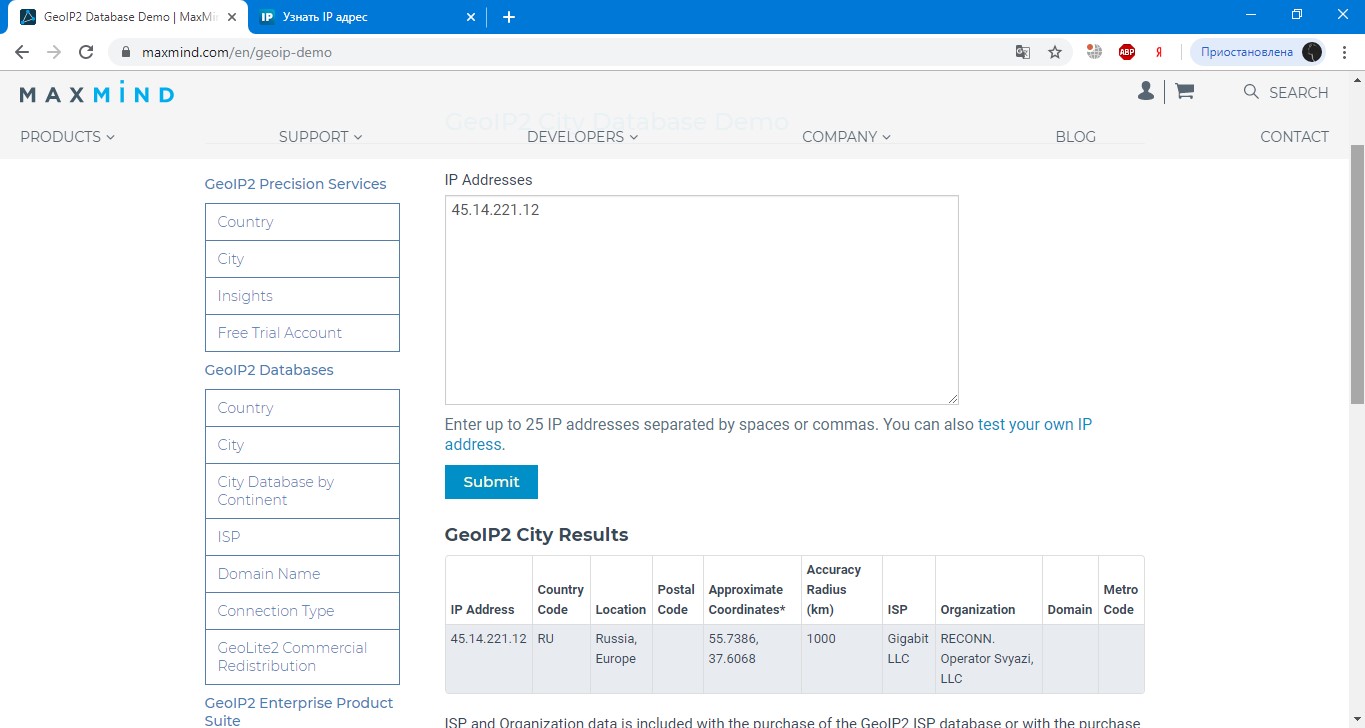
Incorrect or no city or country definition on proxies and DNS
As it was mentioned above, all IP information determination services are just "IP address or subnet - information" type bases, and therefore not all services are able to provide all the necessary information, although the IP address is the same as in the screenshot above.
The first thing you might think is that you were sold a "fake" IP-address or the provider is "messing something up", you should call and demand that the situation be corrected, but it's much simpler, most often it's the lack of information or its incorrectness in the databases of services. In this case, either the resource (for example, 2ip.io) updates its databases very rarely, or deletes old information, and the current information is very difficult to obtain, and providing unverified information is not the best option and it is better to leave N/A in the database. There are also cases when for lack of information it is necessary to provide the information that is in a single copy (as the situation with the farm). And even the subsequent correction of bases will not help to correct the situation, because after that some other service or base can borrow exactly the deleted information for lack of another or unwillingness to take information from another base. Therefore, everything comes down to the policy of a particular service, somewhere it is gentle, somewhere it is unclear and it can be very difficult to trust it, and to refer and prove something is a bit strange for providers who know where the data center or server is actually located, as well as through which nodes the traffic passes.
What to do and who to believe?
This is a very controversial issue. It is always better to request up-to-date information from the place where you purchased the IP address. But we can immediately explain the situation on behalf of the IP-address service: it is indeed sometimes possible to influence the bases through requests to the administrators of the bases, but sometimes such requests are simply left unread or answered with the excuse that the situation will be considered and measures will be taken. Therefore, if there is still a problem on a certain service with incorrect determination of address geolocation or DNS, it is better to check the information on several bases (there is only one base here, all the rest are services that partly use the MaxMind base, and partly their own information, which is also factually collected).
1. https://www.maxmind.com/en/geoip-demo
2. https://yandex.com/internet/
3. https://2ip.io
But even information confirmed by all these resources cannot be 100% correct and up-to-date, as we still deal with bases, and bases are created by parsing, updating information, and discarding it if it is "up-to-date" for a long time. There are also cases of deliberate changes in bases by running traffic through WebRTC. Therefore, always get the most up-to-date and correct information from the source (where you received or purchased the IP-address). Naturally, the information will not be taken from databases, and therefore the maximum that in this case we will provide (by the example of our service) - geolocation, and coordinates, data on ISP, etc. do not provide for objective reasons.
What about DNS?
There are deliberate use of cheaper DNS of other countries by both proxy sellers and providers, but this is rather an exception to the rule and is rare nowadays. Therefore, you should look first of all at the reputation of the proxy seller and make appropriate conclusions or ask for a competent explanation of this error in the database, and also look at the final return from the address, as in case of really incorrect records in the databases it does not affect DNS.
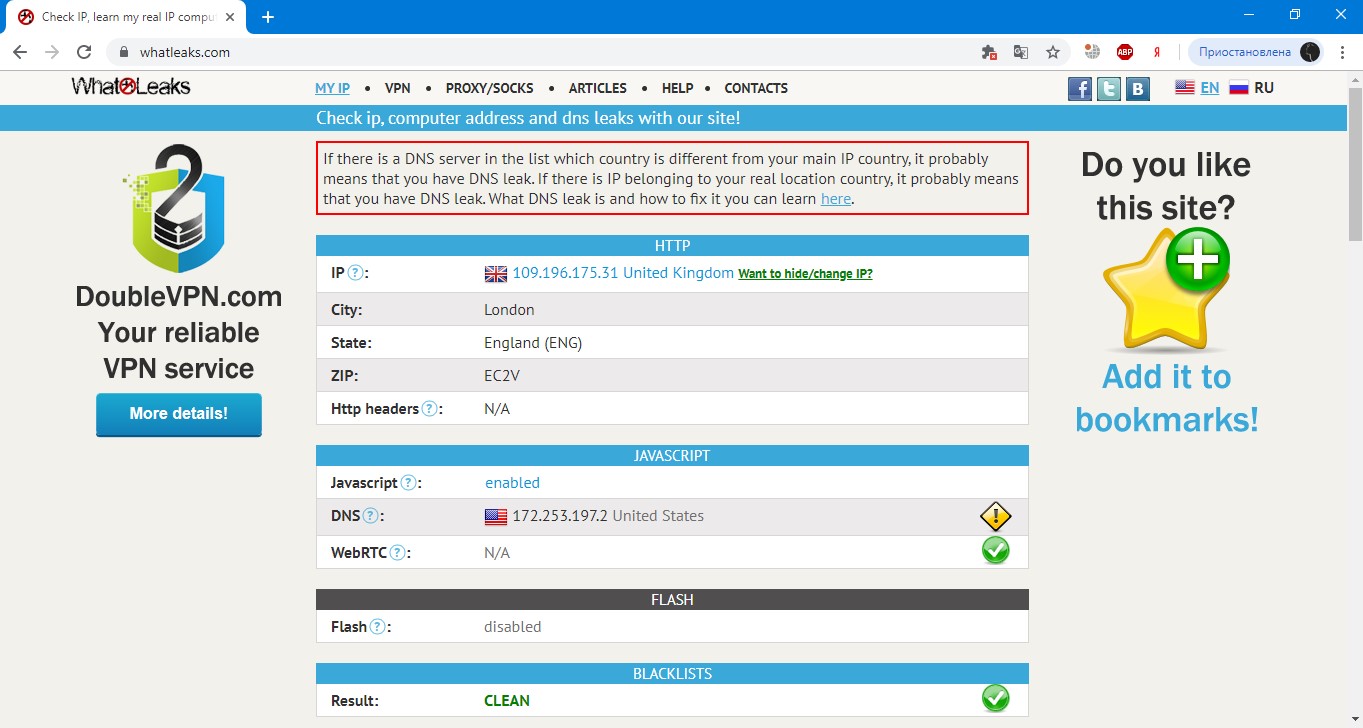
Services and bases
You can criticize databases for hours, but the main thing to remember is that most sites and services use these databases to identify customers. Except that services like social networks have a much larger pool of information on addresses and customer activity at those addresses (requests, messages, browser language, etc.), so it is optimal for companies to compile their own personal databases and draw conclusions not by specific addresses, but by subnets and even ISPs.
Conclusion
What to do if the geolocation in the verification service does not correspond to the geolocation selected when renting? The first thing is to check the address of the proxy not in the service, but for its operability, according to the desired purposes. Say, you rented a proxy for surfing and registering on popular sites that are not available in your country, and they open using a proxy - it means that everything is fine with the proxy. But if these sites continue to be inaccessible, then something is wrong with the IP. Only such a situation can be considered problematic and it is a reason to write to technical support of the proxy provider.
In addition, we emphasize that to ensure complete anonymity, not only proxies should be used, but also an antidetect browser that will change the digital "fingerprint". Note that in addition to geolocation, IP verification services also provide information about the user's time zone, browser, ISP and other unique parameters. This data varies from service to service. If your goal is to achieve complete anonymity and, in addition, multi-accounting, then in addition to changing proxies, you will also need to change the "fingerprints" of your browser.